Pyslvs API¶
Module pyslvs¶
Kernel of Pyslvs.
all_collections()¶
Full name: pyslvs.all_collections
| return |
|---|
collections.abc.Iterator[str] |
Get all collection names.
all_examples()¶
Full name: pyslvs.all_examples
| return |
|---|
collections.abc.Iterator[str] |
Get all example names.
class Collection¶
| Bases |
|---|
TypedDict |
| Members | Type |
|---|---|
cus |
dict[int, int] |
expression |
str |
graph |
collections.abc.Sequence[tuple[int, int]] |
input |
collections.abc.Sequence[tuple[Tuple[int, int], Sequence[float]]] |
placement |
dict[int, Tuple[float, float, float] | None] |
same |
dict[int, int] |
target |
dict[int, Sequence[Tuple[float, float]] | None] |
collection_list()¶
Full name: pyslvs.collection_list
| key | return |
|---|---|
str |
Collection |
The example data of collections.
The format of each configuration is:
expression: Mechanism expression of the structure.- type: str
input: Input pairs.- type: Sequence[Tuple[int, int]]
graph: The generalized chain graph in edge set.- type: Sequence[Tuple[int, int]]
placement: The grounded joints setting. (x,y,r)- type: Dict[int, Optional[Tuple[float, float, float]]]
target: The target joints settings.- type: Dict[int, Optional[Sequence[Tuple[float, float]]]]
cus: The custom joints on specific link. (link number correspond to the graph expression.)- type: Dict[int, int]
same: The multiple joints setting.- type: Dict[int, int]
color_rgb()¶
| name | return |
|---|---|
str |
tuple[int, int, int] |
Get color by name.
Get RGB color data by name, return (0, 0, 0) if it is invalid.
Also support "(R, G, B)" string format.
class Coord¶
| Members | Type |
|---|---|
x |
float |
y |
float |
A data class used to store coordinates.
Coord.__init__()¶
Full name: pyslvs.Coord.__init__
| self | x | y | return |
|---|---|---|---|
Self |
float |
float |
Any |
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
Coord.distance()¶
Full name: pyslvs.Coord.distance
| self | p | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
Coord |
float |
Return the distance between two coordinates.
Coord.is_nan()¶
Full name: pyslvs.Coord.is_nan
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
bool |
Return true if the coordinate value is not a number.
Coord.slope_angle()¶
Full name: pyslvs.Coord.slope_angle
| self | p | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
Coord |
float |
Slope angle of two coordinates.
edges_view()¶
| graph | return |
|---|---|
pyslvs.expression_parser.graph.Graph |
collections.abc.Iterator[tuple[int, Tuple[int, int]]] |
The iterator will yield the sorted edges from graph.
efd_fitting()¶
| path | n | harmonic | return |
|---|---|---|---|
collections.abc.Sequence[Tuple[float, float]] | numpy.ndarray |
int |
int | None |
numpy.ndarray |
0 |
None |
Curve fitting using Elliptical Fourier Descriptor.
The path path will be translated to Fourier descriptor coefficients,
then regenerate a new path as a n x 4 NumPy array.
class EStack¶
| Members | Type |
|---|---|
well_done |
bool |
Triangle solution stack, generated from t_config.
It is pointless to call the constructor.
EStack.as_list()¶
Full name: pyslvs.EStack.as_list
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
list[tuple[str, ...]] |
Copy the dataset as list object.
example_list()¶
Full name: pyslvs.example_list
| key | return |
|---|---|
str |
tuple[str, collections.abc.Sequence[Tuple[int, int]]] |
The example data of mechanisms.
The format of each mechanism is:
[0]: Mechanism expression.- type: str
[1]: Input pairs.- type: Tuple[Tuple[int, int], …]]
expr_solving()¶
Full name: pyslvs.expr_solving
| exprs | vpoints | angles | return |
|---|---|---|---|
pyslvs.tinycadlib.topo_config.EStack |
collections.abc.Sequence[pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.VPoint] |
collections.abc.Mapping[Tuple[int, int], float] | None |
list[_Coord | Tuple[_Coord, _Coord]] |
None |
Solver function of Triangular method and BFGS method, for mechanism
expression vpoints.
The triangle expression stack expr is generated from
t_config.
Solver function will not handle slider input pairs in argument angles,
which is only support revolute joints. In another way, the slider input
pairs can be set by VPoint.disable_offset()
method.
get_include()¶
| return |
|---|
str |
Get include directory.
get_vlinks()¶
| vpoints | return |
|---|---|
collections.abc.Iterable[VPoint] |
list[VLink] |
Get VLinks from a list of VPoint vpoints.
graph2vpoints()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph2vpoints
| graph | pos | cus | same | grounded | return |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
pyslvs.expression_parser.graph.Graph |
dict[int, tuple[float, float]] |
dict[int, int] | None |
dict[int, int] | None |
int | None |
list[pyslvs.expression_parser.expression.VPoint] |
None |
None |
None |
Transform graph into [VPoint] objects. The vertices are mapped to links.
pos: Position for each vertices.cus: Extra points on the specific links.same: Multiple joint setting. The joints are according toedges_view.grounded: The ground link of vertices.
class LinkArgs¶
| Decorators |
|---|
@dataclasses.dataclass(repr=False, eq=False) |
| Members | Type |
|---|---|
color |
str |
name |
str |
points |
str |
Link table argument.
palp()¶
| c1 | a0 | d0 | c2 | inverse | return |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.Coord |
float |
float |
pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.Coord |
bool |
pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.Coord |
False |
The PALP function requires two points, one angle and one distance, obtained the position of fourth point.
In the following picture, c1 correspond to “A”, c2 correspond to “B”,
d0 correspond to “L0”, a0 correspond to “alpha”, return correspond
to “C”.
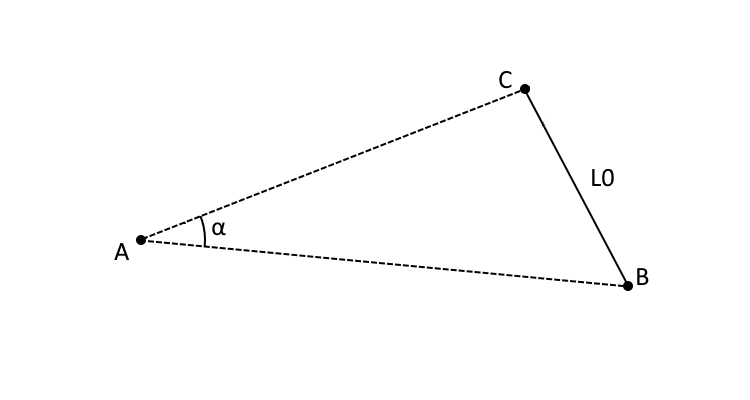
Set inverse option to True can make the result upside down.
parse_params()¶
Full name: pyslvs.parse_params
| expr | return |
|---|---|
str |
list[PointArgs] |
Parse mechanism expression into VPoint constructor arguments.
parse_pos()¶
| expr | return |
|---|---|
str |
list[tuple[float, float]] |
Parse mechanism expression into coordinates.
parse_vlinks()¶
Full name: pyslvs.parse_vlinks
| expr | return |
|---|---|
str |
list[pyslvs.expression_parser.expression.VLink] |
Parse mechanism expression into VLink objects.
parse_vpoints()¶
Full name: pyslvs.parse_vpoints
| expr | return |
|---|---|
str |
list[pyslvs.expression_parser.expression.VPoint] |
Parse mechanism expression into VPoint objects.
plap()¶
| c1 | d0 | a0 | c2 | inverse | return |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.Coord |
float |
float |
pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.Coord | None |
bool |
pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.Coord |
None |
False |
The PLAP function requires two points, one distance and one angle,
obtained the position of third point. The unit of a0 is degree.
In the following picture, c1 correspond to “A”, c2 correspond to “B”,
d0 correspond to “L0”, a0 correspond to “beta”, return correspond
to “C”.
If c2 is not given, “alpha” will be set to zero.
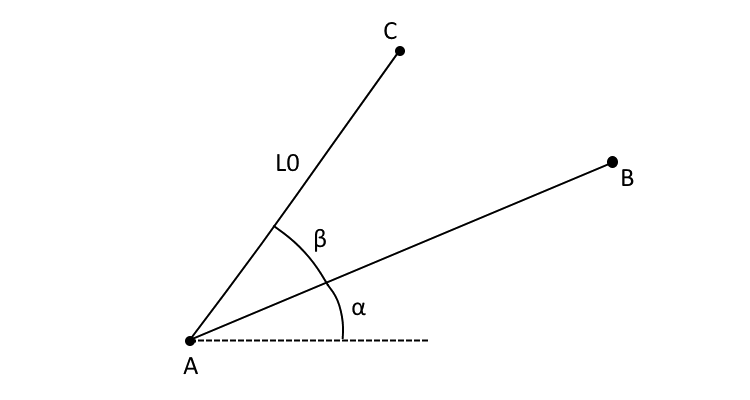
Set inverse option to True can make a0 value as negative.
pllp()¶
| c1 | d0 | d1 | c2 | inverse | return |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.Coord |
float |
float |
pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.Coord |
bool |
pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.Coord |
False |
The PLLP function requires two points and two distances, obtained the position of third point.
In the following picture, c1 correspond to “A”, c2 correspond to “B”,
d0 correspond to “L0”, d1 correspond to “L1”, return correspond to
“C”.
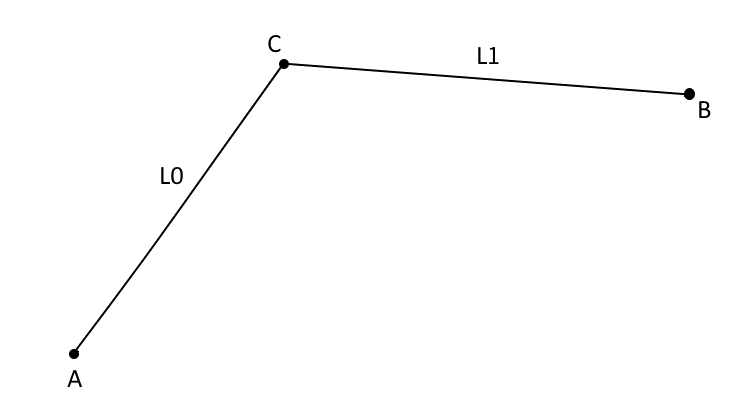
Set inverse option to True can make the result upside down.
plpp()¶
| c1 | d0 | c2 | c3 | inverse | return |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.Coord |
float |
pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.Coord |
pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.Coord |
bool |
pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.Coord |
False |
The PLPP function requires three points and one distance, obtained the position of fourth point.
In the following picture, c1 correspond to “A”, c2 correspond to “B”,
c3 correspond to “C”, d0 correspond to “L0”, return correspond to “D”.
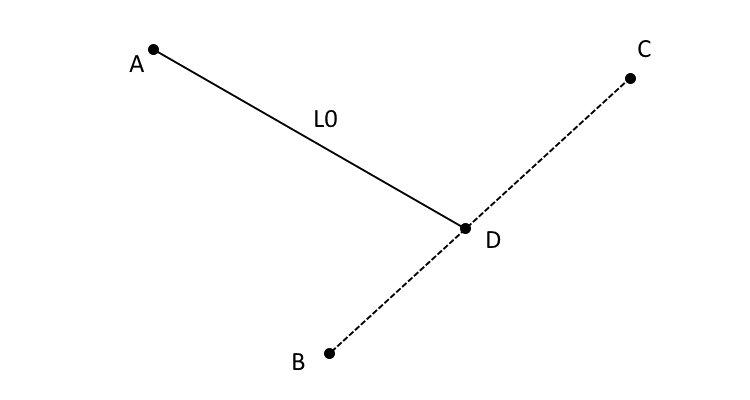
Set inverse option to True can make the result to the another side
between c1 and line c2 c3.
class PointArgs¶
| Decorators |
|---|
@dataclasses.dataclass(repr=False, eq=False) |
| Members | Type |
|---|---|
color |
str |
links |
str |
type |
str |
x |
float |
y |
float |
Point table argument.
ppp()¶
| c1 | c2 | c3 | return |
|---|---|---|---|
pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.Coord |
pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.Coord |
pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.Coord |
pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.Coord |
The PPP function is used to solve parallel linkage.
In the following picture, c1 correspond to “A”, c2 correspond to “B”,
c3 correspond to “C”, return correspond to “D”.

pxy()¶
| c1 | x | y | return |
|---|---|---|---|
pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.Coord |
float |
float |
pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.Coord |
The PXY function requires one point and offset values, get the position of second point.
In the following picture, c1 correspond to “A”, d0 correspond to “X”,
d1 correspond to “Y”, return correspond to “B”, the sign of value are
correspond to coordinate system.
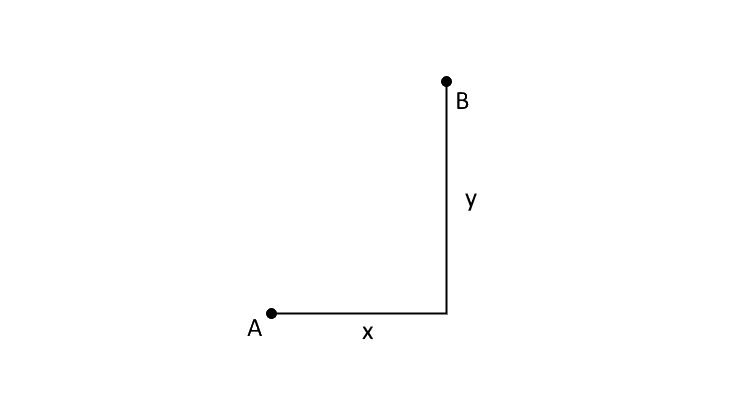
class SolverSystem¶
Full name: pyslvs.SolverSystem
Sketch Solve solver.
Note
The object attributes of such type are unable to access.
SolverSystem.__init__()¶
Full name: pyslvs.SolverSystem.__init__
| self | vpoints | inputs | data_dict | return |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Self |
collections.abc.Sequence[pyslvs.bfgs.expression.VPoint] |
collections.abc.Mapping[Tuple[int, int], float] | None |
collections.abc.Mapping[_PointPair, Union[Coord, float]] | None |
Any |
None |
None |
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
SolverSystem.same_points()¶
Full name: pyslvs.SolverSystem.same_points
| self | vpoints_ | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
collections.abc.Sequence[pyslvs.bfgs.expression.VPoint] |
bool |
Return true if two expressions are same.
SolverSystem.set_data()¶
Full name: pyslvs.SolverSystem.set_data
| self | data_dict | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
collections.abc.Mapping[Tuple[int, int], float] | collections.abc.Mapping[int, Coord] |
None |
Set the values of data_dict parameter from original constructor.
Two groups of dict keys must be the same or subset.
SolverSystem.set_inputs()¶
Full name: pyslvs.SolverSystem.set_inputs
| self | inputs | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
collections.abc.Mapping[tuple[int, int], float] |
None |
Set the values of inputs parameter from original constructor.
Two groups of dict keys must be the same or subset.
SolverSystem.show_data()¶
Full name: pyslvs.SolverSystem.show_data
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
frozenset[int | Tuple[int, int]] |
Show the current keys of data_dict parameter from original
constructor.
SolverSystem.show_inputs()¶
Full name: pyslvs.SolverSystem.show_inputs
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
frozenset[tuple[int, int]] |
Show the current input pairs keys from original constructor.
SolverSystem.solve()¶
Full name: pyslvs.SolverSystem.solve
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
list[_Coord | Tuple[_Coord, _Coord]] |
Solve the conditions and return the result, raise ValueError if not succeeded. The joint position will returned by its index correspondingly.
- Revolute joints: Tuple[float, float]
- Slider joints: Tuple[Tuple[float, float], Tuple[float, float]]
t_config()¶
| vpoints | inputs | status | return |
|---|---|---|---|
collections.abc.Sequence[pyslvs.topo_config.expression.VPoint] |
collections.abc.Sequence[tuple[int, int]] |
dict[int, bool] | None |
EStack |
None |
Generate the Triangle solution stack by mechanism expression vpoints_.
The argument inputs is a list of input pairs.
The argument status will track the configuration of each point,
which is optional.
uniform_expr()¶
Full name: pyslvs.uniform_expr
| v | return |
|---|---|
numpy.ndarray |
list[pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.VPoint] |
Turn the uniform link length into expression.
uniform_four_bar()¶
Full name: pyslvs.uniform_four_bar
| ml | n | return |
|---|---|---|
float |
int |
numpy.ndarray |
Generate n four bar mechanisms from maximum lengths.
These mechanisms have coupling points. Normalized parameters are [L_0, L_2, L_3, L_4, \alpha].
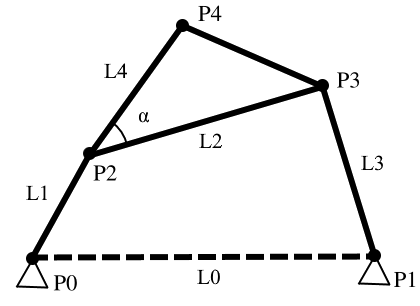
uniform_path()¶
Full name: pyslvs.uniform_path
| v | n | return |
|---|---|---|
numpy.ndarray |
int |
numpy.ndarray |
Generate path with four-bar dimensions.
Normalized parameters are [L_0, L_2, L_3, L_4, \alpha].
class VJoint¶
| Bases |
|---|
enum.IntEnum |
| Enums |
|---|
| R |
| P |
| RP |
An enumeration.
class VLink¶
| Members | Type |
|---|---|
FRAME |
ClassVar[str] |
HOLDER |
ClassVar[VLink] |
color |
tuple[int, int, int] | None |
color_str |
str |
name |
str |
points |
collections.abc.Sequence[int] |
Mechanism expression class in link’s view.
VLink.__contains__()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VLink.__contains__
| self | point | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
int |
bool |
Return key in self.
VLink.__init__()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VLink.__init__
| self | name | color_str | points | color_func | return |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Self |
str |
str |
collections.abc.Iterable[int] |
Callable[[str], _Color] | None |
Any |
None |
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
VLink.points_pos()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VLink.points_pos
| self | vpoints | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
collections.abc.Iterable[VPoint] |
collections.abc.Sequence[Coord] |
Get link positions from a VPoint list.
VLink.set_points()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VLink.set_points
| self | points | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
collections.abc.Iterable[int] |
None |
The update function of points attribute.
class VPoint¶
| Members | Type |
|---|---|
HOLDER |
ClassVar[VPoint] |
angle |
float |
c |
numpy.ndarray |
color |
tuple[int, int, int] | None |
color_str |
str |
links |
collections.abc.Sequence[str] |
type |
VJoint |
type_str |
str |
x |
float |
y |
float |
Mechanism expression class.
VPoint.__getitem__()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.__getitem__
| self | i | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
int |
float |
Return self[key].
VPoint.__init__()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.__init__
| self | links | type_int | angle | color_str | x | y | color_func | return |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Self |
collections.abc.Iterable[str] |
VJoint |
float |
str |
float |
float |
Callable[[str], _Color] | None |
Any |
None |
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
VPoint.copy()¶
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
VPoint |
The copy method of the VPoint object.
VPoint.cx()¶
| Decorators |
|---|
@property |
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
float |
X value of current coordinate. If it’s slider, the pin coordinate will be returned.
VPoint.cy()¶
| Decorators |
|---|
@property |
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
float |
Y value of current coordinate. If it’s slider, the pin coordinate will be returned.
VPoint.disable_offset()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.disable_offset
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
None |
Disable offset setting of the joint.
VPoint.distance()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.distance
| self | p | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
VPoint |
float |
Return the distance between two VPoint objects.
VPoint.expr()¶
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
str |
Return the literal mechanism expression of the joint.
VPoint.grounded()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.grounded
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
bool |
Return true if the joint pin is connected to ground link.
VPoint.has_offset()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.has_offset
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
bool |
Return true if the offset setting is enabled.
VPoint.is_slider()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.is_slider
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
bool |
Return true for slider type.
VPoint.is_slot_link()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.is_slot_link
| self | link | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
str |
bool |
Return true if the slot is on the link link_name.
VPoint.link_pos()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.link_pos
| self | link | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
str |
Coord |
Return the position for the vlink.
VPoint.locate()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.locate
| self | x | y | return |
|---|---|---|---|
Self |
float |
float |
None |
The update function of original coordinate.
VPoint.move()¶
| self | c1 | c2 | return |
|---|---|---|---|
Self |
tuple[float, float] |
tuple[float, float] | None |
None |
None |
The update function of current coordinate(s). The 2nd placement is the pin coordinate of slider joints.
If there is only one argument for a slider joint, the slot and pin coordinates will be set to the same position.
VPoint.no_link()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.no_link
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
bool |
Return true if there is no any link in links attribute.
VPoint.offset()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.offset
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
float |
Return the offset constraint value of the joint.
VPoint.pin_grounded()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.pin_grounded
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
bool |
Return true if the point is at the same link.
VPoint.r_joint()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.r_joint
| Decorators |
|---|
@staticmethod |
| links | x | y | return |
|---|---|---|---|
collections.abc.Iterable[str] |
float |
float |
VPoint |
A fast constructor of revolute joints.
VPoint.replace_link()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.replace_link
| self | link1 | link2 | return |
|---|---|---|---|
Self |
str |
str |
None |
Replace the value in links attribute.
VPoint.rotate()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.rotate
| self | angle | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
float |
None |
The update function of angle attribute.
VPoint.same_link()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.same_link
| self | p | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
VPoint |
bool |
Return true if the point is at the same link.
VPoint.set_links()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.set_links
| self | links | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
collections.abc.Iterable[str] |
None |
The update function of links attribute.
VPoint.set_offset()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.set_offset
| self | offset | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
float |
None |
The update function of slider offset. It will also enable offset value after called.
VPoint.slider_joint()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.slider_joint
| Decorators |
|---|
@staticmethod |
| links | type_int | angle | x | y | return |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
collections.abc.Iterable[str] |
VJoint |
float |
float |
float |
VPoint |
A fast constructor of slider joints.
VPoint.slope_angle()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.slope_angle
| self | p | num1 | num2 | return |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Self |
VPoint |
int |
int |
float |
2 |
2 |
Return the value hypot(p_x - m_x, p_y - m_y),
where m_x, m_y is the value of the joint,
and p_x, p_y is the value of p.
The option num1 and num2 is the position of current coordinate
attribute.
VPoint.sx()¶
| Decorators |
|---|
@property |
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
float |
X value of slot coordinate.
VPoint.sy()¶
| Decorators |
|---|
@property |
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
float |
Y value of slot coordinate.
VPoint.to_coord()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.to_coord
| self | ind | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
int |
Coord |
Obtain coordinate by Coord object.
VPoint.true_offset()¶
Full name: pyslvs.VPoint.true_offset
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
float |
Return the current offset value of the joint.
vpoint_dof()¶
| vpoints | return |
|---|---|
collections.abc.Sequence[pyslvs.tinycadlib.expression.VPoint] |
int |
Return the DOF of the mechanism expression vpoints.
Module pyslvs.efd¶
The source code refer from “spatial_efd” module.
calculate_efd()¶
Full name: pyslvs.efd.calculate_efd
| contour | harmonic | return |
|---|---|---|
numpy.ndarray |
int |
numpy.ndarray |
10 |
Compute the Elliptical Fourier Descriptors for a polygon.
Implements Kuhl and Giardina method of computing the coefficients An, Bn, Cn, Dn for a specified number of harmonics. This code is adapted from the pyefd module. See the original paper for more detail:
Kuhl, FP and Giardina, CR (1982). Elliptic Fourier features of a closed contour. Computer graphics and image processing, 18(3), 236-258.
Args: contour: A n x 2 numpy array represents a path. harmonic: The number of harmonics to compute for the given shape, defaults to 10. Returns: A numpy array of shape (harmonics, 4) representing the four coefficients for each harmonic computed.
fourier_power()¶
Full name: pyslvs.efd.fourier_power
| coeffs | nyq | threshold | return |
|---|---|---|---|
numpy.ndarray |
int |
float |
int |
1.0 |
Compute the total Fourier power and find the minimum number of harmonics required to exceed the threshold fraction of the total power.
This is a good method for identifying the number of harmonics to use to describe a polygon. For more details see:
C. np_costa et al. / Postharvest Biology and Technology 54 (2009) 38-47
Warning: The number of coefficients must be >= the Nyquist Frequency. Args: coeffs: A numpy array of shape (n, 4) representing the four coefficients for each harmonic computed. nyq: The Nyquist Frequency. threshold: The threshold fraction of the total Fourier power, the default is 1. Returns: The number of harmonics required to represent the contour above the threshold Fourier power.
inverse_transform()¶
Full name: pyslvs.efd.inverse_transform
| coeffs | locus_v | n | harmonic | return |
|---|---|---|---|---|
numpy.ndarray |
tuple[float, float] |
int |
int |
numpy.ndarray |
Perform an inverse fourier transform to convert the coefficients back into spatial coordinates.
Implements Kuhl and Giardina method of computing the performing the transform for a specified number of harmonics. This code is adapted from the pyefd module. See the original paper for more detail:
Kuhl, FP and Giardina, CR (1982). Elliptic Fourier features of a closed contour. Computer graphics and image procesnp_sing, 18(3), 236-258.
Args: coeffs: A numpy array of shape (n, 4) representing the four coefficients for each harmonic computed. locus_v: The x,y coordinates of the centroid of the contour being generated. Use calculate_dc_coefficients() to generate the correct locus for a shape. n: The number of coordinate pairs to compute. A larger value will result in a more complex shape at the expense of increased computational time. harmonic: The number of harmonics to be used to generate coordinates. Must be <= coeffs.shape[0]. Supply a smaller value to produce coordinates for a more generalized shape. Returns: A n x 2 numpy array represents a contour.
locus()¶
| contour | return |
|---|---|
numpy.ndarray |
tuple[float, float] |
Compute the dc coefficients, used as the locus when calling inverse_transform().
This code is adapted from the pyefd module. See the original paper for more detail:
Kuhl, FP and Giardina, CR (1982). Elliptic Fourier features of a closed contour. Computer graphics and image procesnp_sing, 18(3), 236-258.
Args: contour: A n x 2 numpy array represents a path. Returns: A tuple containing the c and d coefficients.
normalize_efd()¶
Full name: pyslvs.efd.normalize_efd
| coeffs | norm | return |
|---|---|---|
numpy.ndarray |
bool |
tuple[numpy.ndarray, float] |
True |
Normalize the Elliptical Fourier Descriptor coefficients for a polygon.
Implements Kuhl and Giardina method of normalizing the coefficients An, Bn, Cn, Dn. Performs 3 separate normalizations. First, it makes the data location invariant by re-scaling the data to a common origin. Secondly, the data is rotated with respect to the major axis. Thirdly, the coefficients are normalized with regard to the absolute value of A_1. This code is adapted from the pyefd module. See the original paper for more detail:
Kuhl, FP and Giardina, CR (1982). Elliptic Fourier features of a closed contour. Computer graphics and image procesnp_sing, 18(3), 236-258.
Args: coeffs: A numpy array of shape (n, 4) representing the four coefficients for each harmonic computed. norm: Set to True (the default) to perform the third normalization and false to return the data withot this procesnp_sing step. Set this to False when plotting a comparison between the input data and the Fourier ellipse. Returns: A tuple consisting of a numpy.ndarray of shape (harmonics, 4) representing the four coefficients for each harmonic computed and the rotation in radians applied to the normalized contour.
rotate_contour()¶
Full name: pyslvs.efd.rotate_contour
| contour | angle | centroid | return |
|---|---|---|---|
numpy.ndarray |
float |
tuple[float, float] |
numpy.ndarray |
Rotates a contour about a point by a given amount expressed in degrees.
Operates by calling rotatePoint() on each x,y pair in turn. X and Y must have the same dimensions.
Args: contour: A n x 2 numpy array represents a path. angle: The angle in radians for the contour to be rotated by. centroid: A tuple containing the x,y coordinates of the centroid to rotate the contour about. Returns: A n x 2 numpy array represents a contour.
Module pyslvs.graph¶
Pyslvs graph functions.
contracted_graph()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.contracted_graph
| link_num | stop_func | return |
|---|---|---|
collections.abc.Sequence[int] |
Callable[[], bool] | None |
list[pyslvs.graph.structural.graph.Graph] |
None |
Generate contracted graphs by link assortment link_num.
The check stop function stop_func object for GUI or subprocess,
return True to terminate this function.
contracted_link_assortment()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.contracted_link_assortment
| g | return |
|---|---|
Graph |
list[int] |
Return contracted link assortment of the graph.
contracted_link_synthesis()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.contracted_link_synthesis
| link_num_list | stop_func | return |
|---|---|---|
collections.abc.Sequence[int] |
Callable[[], bool] | None |
list[tuple[int, ...]] |
None |
Return contracted link assortment by link assortment link_num_list.
The check stop function stop_func object for GUI or subprocess,
return True to terminate this function.
conventional_graph()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.conventional_graph
| cg_list | c_j_list | no_degenerate | stop_func | return |
|---|---|---|---|---|
list[pyslvs.graph.structural.graph.Graph] |
collections.abc.Sequence[int] |
int |
Callable[[], bool] | None |
list[pyslvs.graph.structural.graph.Graph] |
1 |
None |
Generate conventional graphs by contracted graphs cg_list and
contracted link assortment c_j_list.
The degenerate setting no_degenerate has following option:
0: No degenerate.1: Only degenerate.- Else: All graphs.
The check stop function stop_func object for GUI or subprocess,
return True to terminate this function.
external_loop_layout()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.external_loop_layout
| graph | node_mode | scale | return |
|---|---|---|---|
pyslvs.graph.layout.graph.Graph |
bool |
float |
dict[int, tuple[float, float]] |
1.0 |
Layout position decided by outer loop (max cycle).
Return the layout position decided by external loop.
Argument node_mode will transform edges into vertices.
Argument scale will resize the position by scale factor.
class Graph¶
| Members | Type |
|---|---|
edges |
tuple[tuple[int, int], ...] |
vertices |
tuple[int, ...] |
The undirected graph class, support multigraph.
Graph.__init__()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.Graph.__init__
| self | edges | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
collections.abc.Iterable[tuple[int, int]] |
Any |
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
Graph.add_edge()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.Graph.add_edge
| self | n1 | n2 | return |
|---|---|---|---|
Self |
int |
int |
None |
Add edge n1 to n2.
Graph.add_vertices()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.Graph.add_vertices
| self | vertices | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
collections.abc.Iterable[int] |
None |
Add vertices from iterable object vertices.
Graph.adjacency_matrix()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.Graph.adjacency_matrix
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
numpy.ndarray |
Generate a adjacency matrix.
Assume the matrix A[i, j] = A[j, i].
Where A[i, j] = 1 if edge (i, j) exist.
Graph.copy()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.Graph.copy
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
Graph |
The copy method of the Graph object.
Graph.degree_code()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.Graph.degree_code
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
int |
Generate a degree code.
With a sorted vertices mapping by the degrees of each vertex, regenerate a new adjacency matrix. A binary code can be found by concatenating the upper right elements. The degree code is the maximum value of the permutation.
Graph.degrees()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.Graph.degrees
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
dict[int, int] |
Return the degrees of each vertex.
Graph.dof()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.Graph.dof
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
int |
Return DOF of the graph.
Note
DOF is the Degree of Freedoms to a mechanism.
In the [Graph] objects, all vertices will assumed as revolute joints (1 DOF).
Graph.duplicate()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.Graph.duplicate
| self | vertices | times | return |
|---|---|---|---|
Self |
collections.abc.Iterable[int] |
int |
Graph |
Make graph duplicate by specific vertices. Return a new graph.
Graph.has_cut_link()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.Graph.has_cut_link
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
bool |
Return true if the graph has any cut links.
Graph.has_triangle()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.Graph.has_triangle
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
bool |
Return true if the graph has triangle.
Graph.is_connected()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.Graph.is_connected
| self | without | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
int |
bool |
-1 |
Return True if the graph is connected.
Set the argument without to ignore one vertex.
Graph.is_degenerate()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.Graph.is_degenerate
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
bool |
Return true if this kinematic chain is degenerate.
- Prue all multiple contracted links recursively.
- Check the DOF of sub-graph if it is lower then zero.
Graph.is_isomorphic()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.Graph.is_isomorphic
| self | graph | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
Graph |
bool |
Return true if two graphs is isomorphic.
Default is using VF2 algorithm.
Graph.is_isomorphic_degree_code()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.Graph.is_isomorphic_degree_code
| self | graph | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
Graph |
bool |
Compare isomorphism by degree code algorithm.
Graph.is_isomorphic_vf2()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.Graph.is_isomorphic_vf2
| self | graph | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
Graph |
bool |
Compare isomorphism by VF2 algorithm, one of the high performance isomorphic algorithms.
Graph.neighbors()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.Graph.neighbors
| self | n | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
int |
tuple[int, ...] |
Return the neighbors of the vertex n.
is_planar()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.is_planar
| g | return |
|---|---|
pyslvs.graph.planar.graph.Graph |
bool |
Return true if the graph is a planar graph.
labeled_enumerate()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.labeled_enumerate
| g | return |
|---|---|
Graph |
list[tuple[int, Graph]] |
Enumerate each node with labeled except isomorphism.
link_assortment()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.link_assortment
| g | return |
|---|---|
Graph |
list[int] |
Return link assortment of the graph.
link_synthesis()¶
Full name: pyslvs.graph.link_synthesis
| nl | nj | stop_func | return |
|---|---|---|---|
int |
int |
Callable[[], bool] | None |
list[tuple[int, ...]] |
None |
Return link assortment by number of links nl and number of joints nj.
The check stop function stop_func object for GUI or subprocess,
return True to terminate this function.
Module pyslvs.metaheuristics¶
Kernel of Metaheuristic Algorithm.
algorithm()¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.algorithm
| opt | return |
|---|---|
AlgorithmType |
type[pyslvs.metaheuristics.utility.Algorithm] |
Return the class of the algorithms.
class Algorithm¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.Algorithm
| Bases |
|---|
Generic[FVal] |
| Members | Type |
|---|---|
func |
ObjFunc[FVal] |
Algorithm base class.
It is used to build the Meta-heuristic Algorithms.
Algorithm.__class_getitem__()¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.Algorithm.__class_getitem__
| cls | item | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
Any |
Any |
Algorithm.__init__()¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.Algorithm.__init__
| Decorators |
|---|
@abc.abstractmethod |
| self | func | settings | progress_fun | interrupt_fun | return |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Self |
ObjFunc[FVal] |
pyslvs.metaheuristics.utility.config_types.Setting |
Callable[[int, str], None] | None |
Callable[[], bool] | None |
Any |
None |
None |
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
Algorithm.history()¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.Algorithm.history
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
numpy.ndarray |
Return the history of the process.
The first value is generation (iteration); the second value is fitness; the third value is time in second.
Algorithm.result()¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.Algorithm.result
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
tuple[numpy.ndarray, float] |
Return the best variable vector and its fitness.
Algorithm.run()¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.Algorithm.run
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
FVal |
Run and return the result and convergence history.
The first place of return is came from
calling ObjFunc.result().
The second place of return is a list of generation data,
which type is Tuple[int, float, float]].
The first of them is generation,
the second is fitness, and the last one is time in second.
class AlgorithmType¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.AlgorithmType
| Decorators |
|---|
@enum.unique |
| Bases |
|---|
str |
enum.Enum |
| Enums |
|---|
| RGA |
| DE |
| PSO |
| FA |
| TLBO |
Enum type of algorithms.
class DE¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.DE
| Bases |
|---|
pyslvs.metaheuristics.de.utility.Algorithm |
The implementation of Differential Evolution.
DE.__init__()¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.DE.__init__
| self | func | settings | progress_fun | interrupt_fun | return |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Self |
pyslvs.metaheuristics.de.utility.ObjFunc[pyslvs.metaheuristics.de.utility.FVal] |
pyslvs.metaheuristics.de.config_types.DESetting |
Callable[[int, str], None] | None |
Callable[[], bool] | None |
Any |
None |
None |
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
default()¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.default
| opt | return |
|---|---|
AlgorithmType |
dict[str, int | float] |
Return the default settings of the algorithms.
class DESetting¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.DESetting
| Bases |
|---|
Setting |
| Members | Type |
|---|---|
cr |
float |
f |
float |
strategy |
pyslvs.metaheuristics.config_types.de.Strategy |
class FA¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.FA
| Bases |
|---|
pyslvs.metaheuristics.fa.utility.Algorithm |
The implementation of Firefly Algorithm.
FA.__init__()¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.FA.__init__
| self | func | settings | progress_fun | interrupt_fun | return |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Self |
pyslvs.metaheuristics.fa.utility.ObjFunc[pyslvs.metaheuristics.fa.utility.FVal] |
pyslvs.metaheuristics.fa.config_types.FASetting |
Callable[[int, str], None] | None |
Callable[[], bool] | None |
Any |
None |
None |
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
class FASetting¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.FASetting
| Bases |
|---|
Setting |
| Members | Type |
|---|---|
alpha |
float |
beta0 |
float |
beta_min |
float |
gamma |
float |
class ObjFunc¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.ObjFunc
| Bases |
|---|
Generic[FVal] |
Objective function base class.
It is used to build the objective function for Meta-heuristic Algorithms.
ObjFunc.fitness()¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.ObjFunc.fitness
| Decorators |
|---|
@abc.abstractmethod |
| self | v | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
numpy.ndarray |
numpy.double |
(cdef function) Return the fitness from the variable list v.
This function will be directly called in the algorithms.
ObjFunc.result()¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.ObjFunc.result
| self | v | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
numpy.ndarray |
FVal |
The result function. Default is the best variable vector v.
class PSO¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.PSO
| Bases |
|---|
pyslvs.metaheuristics.pso.utility.Algorithm |
Algorithm base class.
It is used to build the Meta-heuristic Algorithms.
PSO.__init__()¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.PSO.__init__
| self | func | settings | progress_fun | interrupt_fun | return |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Self |
pyslvs.metaheuristics.pso.utility.ObjFunc[pyslvs.metaheuristics.pso.utility.FVal] |
pyslvs.metaheuristics.pso.config_types.PSOSetting |
Callable[[int, str], None] | None |
Callable[[], bool] | None |
Any |
None |
None |
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
class RGA¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.RGA
| Bases |
|---|
pyslvs.metaheuristics.rga.utility.Algorithm |
The implementation of Real-coded Genetic Algorithm.
RGA.__init__()¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.RGA.__init__
| self | func | settings | progress_fun | interrupt_fun | return |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Self |
pyslvs.metaheuristics.rga.utility.ObjFunc[pyslvs.metaheuristics.rga.utility.FVal] |
pyslvs.metaheuristics.rga.config_types.RGASetting |
Callable[[int, str], None] | None |
Callable[[], bool] | None |
Any |
None |
None |
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
class RGASetting¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.RGASetting
| Bases |
|---|
Setting |
| Members | Type |
|---|---|
cross |
float |
delta |
float |
mutate |
float |
win |
float |
class Setting¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.Setting
| Bases |
|---|
TypedDict |
| Members | Type |
|---|---|
max_gen |
int |
max_time |
float |
min_fit |
float |
parallel |
bool |
pop_num |
int |
report |
int |
slow_down |
float |
class TLBO¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.TLBO
| Bases |
|---|
pyslvs.metaheuristics.tlbo.utility.Algorithm |
The implementation of Teaching Learning Based Optimization.
TLBO.__init__()¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.TLBO.__init__
| self | func | settings | progress_fun | interrupt_fun | return |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Self |
pyslvs.metaheuristics.tlbo.utility.ObjFunc[pyslvs.metaheuristics.tlbo.utility.FVal] |
pyslvs.metaheuristics.tlbo.config_types.TOBLSetting |
Callable[[int, str], None] | None |
Callable[[], bool] | None |
Any |
None |
None |
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
class TOBLSetting¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.TOBLSetting
| Bases |
|---|
Setting |
Module pyslvs.optimization¶
Pyslvs optimization targets.
cross_correlation()¶
Full name: pyslvs.optimization.cross_correlation
| p1 | p2 | t | return |
|---|---|---|---|
numpy.ndarray |
numpy.ndarray |
float |
numpy.ndarray |
0.1 |
Compare signature and return as an 1d array.
>>> from pyslvs.optimization import curvature, path_signature
>>> ps1 = path_signature(curvature(...))
>>> ps2 = path_signature(curvature(...))
>>> from pyslvs.optimization import cross_correlation
>>> cc = cross_correlation(ps1, ps2)
curvature()¶
Full name: pyslvs.optimization.curvature
| path | return |
|---|---|
collections.abc.Iterable[tuple[float, float]] |
numpy.ndarray |
Calculate the signed curvature and return as an array.
derivative()¶
Full name: pyslvs.optimization.derivative
| path | return |
|---|---|
numpy.ndarray |
numpy.ndarray |
Differential function. Return p'.
class FConfig¶
Full name: pyslvs.optimization.FConfig
| Bases |
|---|
TypedDict |
| Members | Type |
|---|---|
expression |
collections.abc.Sequence[pyslvs.expression.VPoint] |
input |
collections.abc.Sequence[tuple[Tuple[int, int], Sequence[float]]] |
lower |
float |
placement |
dict[int, tuple[float, float, float]] |
same |
dict[int, int] |
shape_only |
bool |
target |
dict[int, collections.abc.Sequence[Tuple[float, float]]] |
upper |
float |
class FPlanar¶
Full name: pyslvs.optimization.FPlanar
| Bases |
|---|
pyslvs.metaheuristics.ObjFunc[str] |
| Members | Type |
|---|---|
callback |
int |
A fast matching method that adds mapping angles to variables.
Allowing defects.
FPlanar.__init__()¶
Full name: pyslvs.optimization.FPlanar.__init__
| self | mech | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
pyslvs.optimization.f_planar.utility.FConfig |
Any |
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
FPlanar.fitness()¶
Full name: pyslvs.optimization.FPlanar.fitness
| self | v | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
numpy.ndarray |
numpy.double |
The fitness is the error between target path and self.
Chromosome format: (decided by upper and lower)
v: [Ax, Ay, Dx, Dy, ..., L0, L1, ..., A00, A01, ..., A10, A11, ...]
FPlanar.is_two_kernel()¶
Full name: pyslvs.optimization.FPlanar.is_two_kernel
| self | return |
|---|---|
Self |
bool |
Input a generic data (variable array), return the mechanism expression.
FPlanar.result()¶
Full name: pyslvs.optimization.FPlanar.result
| self | v | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
numpy.ndarray |
str |
Input a generic data (variable array), return the mechanism expression.
class NConfig¶
Full name: pyslvs.optimization.NConfig
| Bases |
|---|
TypedDict |
| Members | Type |
|---|---|
target |
collections.abc.Sequence[tuple[float, float]] |
norm_path()¶
Full name: pyslvs.optimization.norm_path
| path | scale | return |
|---|---|---|
collections.abc.Iterable[tuple[float, float]] |
float |
numpy.ndarray |
1 |
Normalization function.
norm_pca()¶
Full name: pyslvs.optimization.norm_pca
| path | return |
|---|---|
collections.abc.Iterable[tuple[float, float]] |
numpy.ndarray |
Normalization function by PCA.
class NPlanar¶
Full name: pyslvs.optimization.NPlanar
| Bases |
|---|
pyslvs.metaheuristics.ObjFunc[str] |
A normalized matching method.
Defects free. Normalized parameters are [L_0, L_2, L_3, L_4, \alpha].

NPlanar.__init__()¶
Full name: pyslvs.optimization.NPlanar.__init__
| self | mech | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
pyslvs.optimization.n_planar.utility.NConfig |
Any |
Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
NPlanar.fitness()¶
Full name: pyslvs.optimization.NPlanar.fitness
| self | v | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
numpy.ndarray |
numpy.double |
NPlanar.result()¶
Full name: pyslvs.optimization.NPlanar.result
| self | v | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
numpy.ndarray |
str |
path_signature()¶
Full name: pyslvs.optimization.path_signature
| k | maximum | return |
|---|---|---|
numpy.ndarray |
float |
numpy.ndarray |
100 |
Require a curvature, return path signature. It’s composed by curvature \kappa and a K value.
>>> from pyslvs.optimization import curvature, path_signature
>>> path_signature(curvature(...))
Module pyslvs.metaheuristics.config_types¶
class PSOSetting¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.config_types.PSOSetting
| Bases |
|---|
Setting |
| Members | Type |
|---|---|
cognition |
float |
social |
float |
velocity |
float |
Module pyslvs.metaheuristics.de¶
class Strategy¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.de.Strategy
| Bases |
|---|
enum.IntEnum |
| Enums |
|---|
| S1 |
| S2 |
| S3 |
| S4 |
| S5 |
| S6 |
| S7 |
| S8 |
| S9 |
| S0 |
An enumeration.
Module pyslvs.metaheuristics.test¶
class TestObj¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.test.TestObj
| Bases |
|---|
pyslvs.metaheuristics.test.utility.ObjFunc[float] |
Test objective function.
f(x) = x1^2 + 8*x2
TestObj.fitness()¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.test.TestObj.fitness
| self | v | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
numpy.ndarray |
numpy.double |
TestObj.result()¶
Full name: pyslvs.metaheuristics.test.TestObj.result
| self | v | return |
|---|---|---|
Self |
numpy.ndarray |
float |